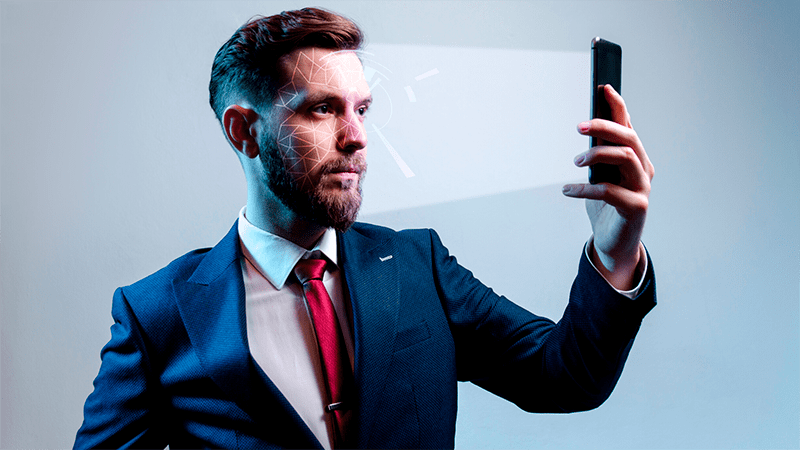
Verificación de identidad digital
Evita el fraude y cumple con las normativas proporcionando una gran experiencia de usuario que permita verificar la identidad de tus clientes en segundos. Soluciones de onboarding digital, firma electrónica y autenticación biométrica.
Conocer la identidad real de tus clientes en internet sin la tecnología adecuada puede ser muy frustrante
Normativa
eIDAS, KYC, AML, GDPR… ¡no te agobies!
No dejes que el cumplimiento regulatorio te quite el sueño. Con nuestras soluciones estarás al día con tus obligaciones y dormirás tranquilo.
Ahorro
Deja de malgastar tiempo y dinero
Elimina el coste de revisión manual durante el onboarding y digitaliza tu firma: ganarás tiempo para lo que realmente importa.
Automatización
La revisión manual no es escalable
Automatiza el proceso de verificación de identidad y en apenas segundos permitirás que tus clientes disfruten de tus servicios.
Fraude
Que nadie te engañe con una identidad falsa
Evita el fraude detectando falsos documentos de identidad e identidades falsas con reconocimiento facial.
Experiencia de usuario
Ofrece una experiencia «wow» a tus clientes
Usabilidad
Ofrece una experiencia «wow» a tus clientes
Captura automáticamente las imágenes, autorellena formularios y olvida las contraseñas al identificarte con biometría.
Digitalización
Una identidad digital en la que puedes confiar
Une la identidad real de tu cliente con su identidad digital a través de su documento de identidad y su cara.
Nadie debería sufrir fraude cuando tiene un proyecto. Sabemos cómo te sientes y por ello queremos hacer del mundo un lugar más seguro, en el que realizar transacciones digitales con la misma confianza que en persona.
Tenemos más de 16 años de experiencia con clientes de múltiples sectores en más de 30 países y millones de identidades verificadas. Hemos desarrollado nuestra propia tecnología de verificación de identidad digital para ser flexibles y cubrir todas tus necesidades, sea cual sea tu caso de uso. Pero, sobre todo, somos apasionados y honestos.
USADO POR EMPRESAS LÍDERES






Soluciones de identificación para cada etapa de la relación con tus clientes
Desde un inicio, en un proceso de registro, pasando por la firma digital hasta la autenticación cuando sea necesario con cualquiera de nuestras soluciones de verificación de identidad
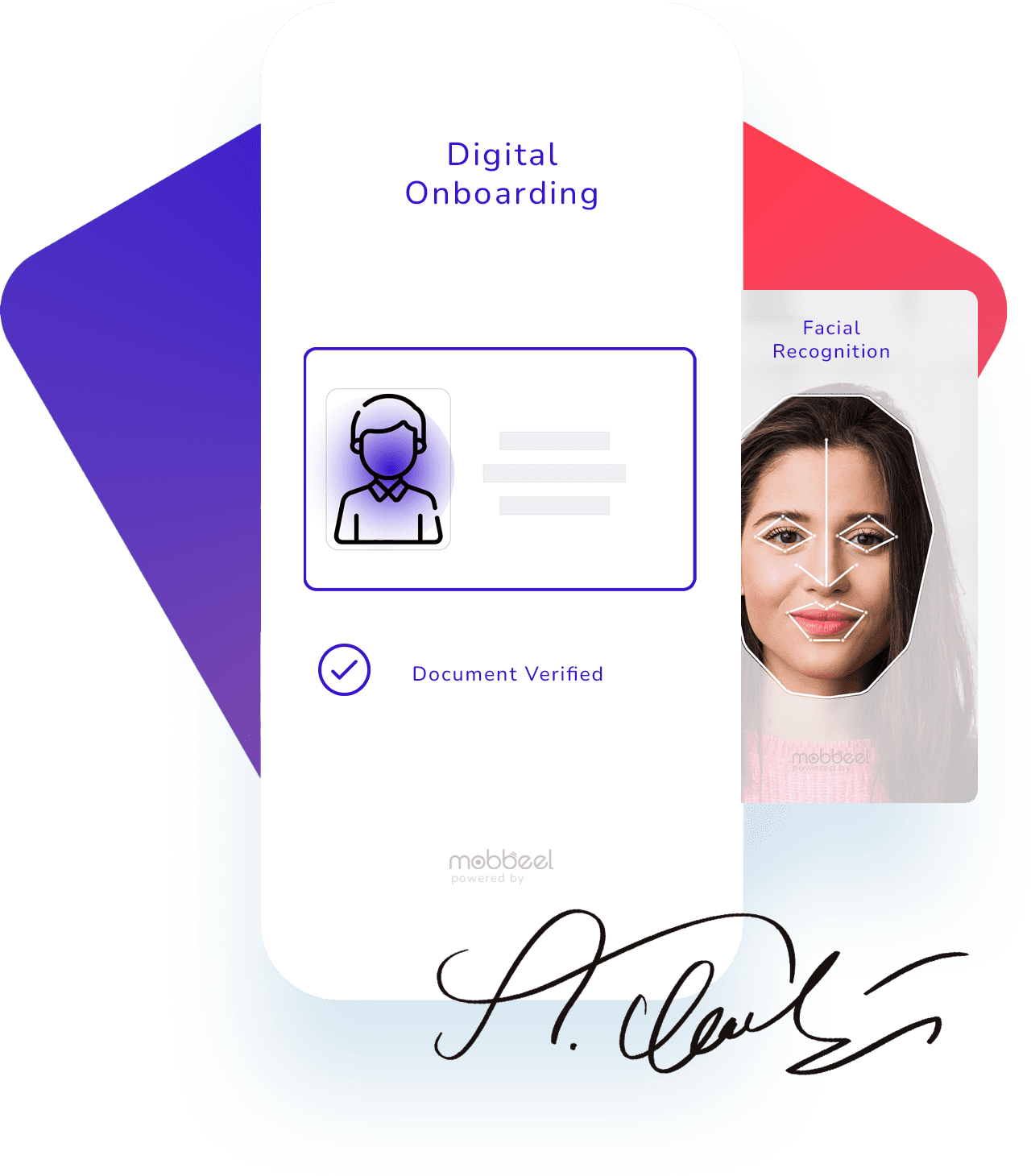
Onboarding Digital
Incorpora tus nuevos clientes digitales a través de nuestra tecnología eKYC / AML de onboarding digital en segundos, escaneando un documento de identidad y verificando la identidad del poseedor con biometría facial.
Firma Biométrica
A continuación, formaliza su relación contractual con la empresa con nuestra solución de firma electrónica avanzada:
- Firma biométrica manuscrita.
- Firmas OTP / OTP Robusto / OTC.
Autenticación Biométrica
Y por último, autentifica a tus usuarios cada vez que accedan a tu sistema o autoricen una transacción con reconocimiento facial, de voz, de huella dactilar o de firma.
Tecnología a prueba de normas
Nuestra solución de onboarding te permite cumplir con las normativas de anti-blanqueo de capitales (AML) y conoce a tu cliente (KYC) mientras que nuestra firma digital es una firma electrónica avanzada según la normativa eIDAS.

Protección de datos: gdpr
Respetamos tu privacidad y la de tus clientes
Seguridad de la información: iso 27001
La seguridad de nuestros sistemas y de tu información es vital para nosotros.
Con soporte legal
Ecija Abogados audita nuestra tecnología para validar su cumplimiento con las normas y su integridad.
Diferénciate de tu competencia con tecnología que tus clientes amarán
Que tu empresa esté a la última puede hacer que se decanten por tus servicios.
Seguridad y cumplimiento
¿Cómo garantiza el cumplimiento de normativas?
Mobbeel cumple con las principales normativas de protección de datos y seguridad a nivel internacional, incluyendo GDPR, KYC/AML, ISO27001, eIDAS, EBA, SEPBLAC, ENS, IA Act, NIST, entre otras.
¿Qué certificaciones tiene?
Mobbeel posee diversas certificaciones, entre las que destacan evaluaciones de algoritmos por el NIST, homologación en el Catálogo de Productos y Servicios de Seguridad de las Tecnologías de la Información y las Comunicaciones (CPSTIC), certificación ISO 27001, seguimos ISO 30107, certificación de la Comisión Alemana para la Protección de Menores en Internet (KJM).
¿Cómo previene Mobbeel el fraude de identidad?
Todas las soluciones de Mobbeel cuentan con un módulo antifraude que detecta posibles ataques como ataques de presentación, deepfakes, ataques de inyección y manipulación de documentos de identidad. Además, para la protección de los datos se utiliza encriptación y plantillas biométricas no reversibles para proteger la privacidad del usuario.
UX y personalización
¿Las soluciones de Mobbeel son intuitivas y accesibles?
Sí. Todas las soluciones de Mobbeel están diseñadas con interfaces sencillas e intuitivas para reducir la tasa de abandono. Además, se guía a los usuarios con mensajes en tiempo real dependiendo de las condiciones ambientales para ayudarle a finalizar con éxito.
¿Qué opciones de personalización ofrece el sistema?
Nuestros clientes pueden elegir los pasos o módulos que mejor se adapten a sus necesidades sin depender de una infraestructura cerrada. Además, existe la posibilidad de configurar idiomas, colores, fuentes, imágenes, diálogos, de incorporar cuenta atrás y de llevar a cabo personalizaciones de la plataforma como redireccionamiento por código QR.
¿Los procesos son automatizados?
La responsabilidad se delega en la tecnología no siendo necesario la intervención manual en el proceso. Sin embargo, es posible incorporar supervisión humana, por ejemplo, para la revisión, aceptación o rechazo de procesos con el fin de cumplir normativas o garantizar altos estándares de seguridad.
Información técnica
¿Cuánto tiempo puede llevar a cabo la integración?
Los tiempos de implementación son rápidos. Todo depende de la experiencia del equipo integrador y del tipo de integración seleccionada. Por ejemplo, la integración del Gateway de Mobbeel puede llevar de pocas horas a un par de días dependiendo del caso de uso.
¿Cuáles son los requisitos técnicos para la integración?
Las soluciones de Mobbeel son flexibles y modulares y por ello están diseñadas para integrarse en cualquier entorno digital a través de SDKs nativas o híbridas, un gateway web o vía APIs, garantizando una amplia compatibilidad y una experiencia de usuario fluida en diversos dispositivos y sistemas operativos.
¿El servicio incluye soporte técnico?
El servicio incluye soporte completo durante todo el ciclo de vida del cliente, desde la implementación, pasando por la formación del personal, hasta la asistencia post-lanzamiento.
APRENDE MÁS SOBRE LA IDENTIDAD DIGITAL

Guía Reconocimiento Facial
Descubre la guía interactiva sobre Reconocimiento Facial haciendo un recorrido por su historia, funcionamiento, regulaciones, aplicaciones y desafíos en ciberseguridad.

Curso de Onboarding Digital (Gratis)
Entender la tecnología antes de implementarla garantiza que aproveches al máximo su potencial.
Esta tecnología es el primer punto de contacto con tu cliente y define el rumbo de vuestra relación.
Mantente al día sobre noticias y tendencias de la industria de la identidad digital
ÚLTIMOS ARTÍCULOS DEL BLOG
La UE refuerza la seguridad de los documentos de identidad y los adapta al estándar ICAO
El papel ha sido sinónimo de seguridad durante siglos. Contratos, escrituras o leyes han encontrado en el soporte físico una garantía de verdad y autenticidad. En muchos sectores, el documento impreso sigue siendo útil como prueba tangible difícil de cuestionar. Sin...
La identidad digital de Mobbeel en MWC Barcelona 2026
Yuval Noah Harari sostiene en Nexus que la historia de la humanidad puede entenderse como la historia de sus redes de información. Cada avance en el tiempo como la escritura, la imprenta o Internet ha cambiado la forma en que nos comunicamos y nos organizamos, pero...
Regulación del juego online en Argentina
El juego online en Argentina atraviesa un punto de inflexión. En los últimos años, y con mayor intensidad reciente, distintas provincias avanzaron en nuevas regulaciones sobre las plataformas de apuestas online, impulsadas por la necesidad de ordenar un mercado en...
¿Hablamos?
No tienes que seguir frustrado con tus procesos de verificación de identidad digital. Deja de perder tiempo, dinero y energía en estrategias ineficaces y verifica tus clientes en el acto.












