Any business today has a compelling reason to know its customers well: to protect against fraud and comply with regulations. However, in digital environments, merely asking for a name and some basic information is no longer sufficient to confirm the identity of the person on the other side of the screen.
How can you be sure that the person on the other end is truly who they claim to be? This is where identity proofing comes in, acting like a detective who checks multiple sources to ensure that the claimed identity is genuine.
Online identity proofing can encompass tasks such as checking various sources of information, utilizing biometric technology for identity confirmation, or verifying identity documents. It’s akin to thoroughly examining all the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle to ensure they fit perfectly.
What is Identity Proofing and why is it important?
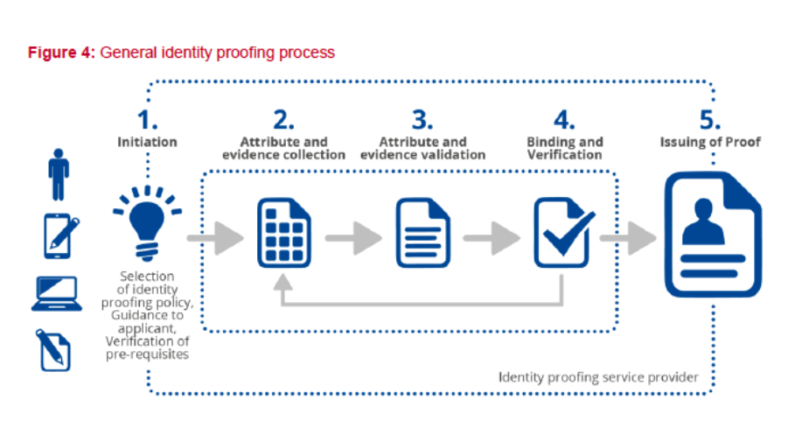
Identity proofing is a process that verifies and authenticates the identity of a person attempting to access a service or system. It is also known as identity verification and involves confirming that an identity exists in the real world and truly belongs to the person presenting it.
Typically, this process is carried out when you register with a website or service in a process commonly known as digital onboarding. Its purpose is to ensure that you are using a legitimate and accurate identity.
Imagine you’re making an online purchase or signing up for a web platform. At that point, the company needs to be certain that you are who you claim to be. This is what we call “identity proofing,” and it should involve a thorough check.

Sometimes, they will request personal information like your name or address or even ask you questions that only you should know. However, this isn’t always sufficient because there’s a risk that this information may have been compromised or accessed by others.
For this reason, more advanced solutions are used to verify your identity. The next step might involve companies asking you to take a selfie or record a video of yourself to demonstrate that you are a real, live person (a process known as liveness detection). They may also examine your documents to ensure everything matches. You’ll be asked to show them to the camera, and they will be automatically scanned and validated.
How Is Identity Proofing Done?
There are different methods and levels of rigor, but in general, they are based on the following elements:
- Knowledge-based attributes: These are personal data that only the user should know, such as their date of birth, address, or social security number. This data can be checked against public or private sources to validate its accuracy..
- Identity document verification: This process involves checking the authenticity and validity of an identity document, such as a passport, ID card, or driver’s license. It can be done through optical character recognition (OCR) techniques, NFC chip reading, or hologram and watermark verification.
- Biometric verification: This process confirms that the user is indeed who they claim to be through a biometric test, such as facial recognition or voice biometrics. These tests can be conducted via web environments or native mobile applications.
What Is the Difference Between Identity Proofing and Biometric Authentication?
The difference between identity proofing and biometric authentication lies in the process in which they are performed.
Identity proofing refers to the initial process of verifying a person’s identity when registering or initiating a relationship with a company, public body, or online service, typically in a digital onboarding process. It ensures that the person claiming an identity is indeed who they say they are. Furthermore, it often involves verification from multiple sources, including biometrics, and is typically performed only once.
Biometric authentication, on the other hand, pertains to the process of verifying a person’s identity when attempting to access a system or service, typically after completing the identity proofing process. It relies on unique and measurable physical characteristics of a person, such as fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, or voice. Biometric authentication can be used to verify identity multiple times throughout the customer’s use of the service.
Benefits of Identity Proofing
Identity proofing has several benefits for both users and service or system providers:
- For users, identity proofing allows them to access services or systems securely and conveniently, without having to remember multiple passwords or answer difficult questions. It also protects them against identity theft and fraudulent transactions by making it more difficult for someone to impersonate them or access their data without their consent.
- For providers, identity proofing enables them to comply with legal regulations (KYC and AML) and security standards that require them to verify the identity of their customers or users. It also helps them improve customer or user trust and satisfaction by offering a smoother and more personalized access experience
eIDAS and Identity Proofing
The European standards published by ETSI on trust services address how we confirm people’s identity. However, there’s an issue: these standards mention phrases like “physical presence” or “means equivalent to physical presence,” as per article 24.1 of eIDAS. The problem is that they don’t provide a clear explanation of what “physical presence” means, leaving room for subjective interpretation.
eIDAS doesn’t lay out precise requirements for physical identity documents or the individuals responsible for conducting these checks. In other words, determining what qualifies as an “equivalent guarantee” to physical presence depends on one’s interpretation, creating confusion.

This issue has become even more critical with the revision of the eIDAS Regulation, also known as eIDAS2. Consequently, it was necessary to address this matter in a more straightforward and effective manner.
Identity accreditation isn’t a trust service on its own within the eIDAS regulation but rather an integral component of trust services. Various trust services may incorporate an identity proofing service component, which is why trust service providers (TSPs) often outsource identity verification to specialized providers in this field.
Security Requirements/Risks
To ensure overall security, security requirements are established that address four primary categories of risks:
- Forged evidence: When someone pretends to be someone else using false documents.
- Identity theft: When someone uses valid but stolen information.
- Operational risks: Technical issues or human errors that may arise.
- Social risks: Risks related to interactions between individuals during the verification process.
New European Standards on Identity Proofing
In 2021, new technical standards were published to define what the equivalence of physical or face-to-face identity proofing would entail:
- ETSI RT 119 460: Electronic Signature and Infrastructures (ESI); Survey of technologies and regulatory requirements for identity proofing for trust service providers.
- ETSI RT 119 461: Electronic Signature and Infrastructures (ESI); Policy and security requirements for identity proofing for trust service providers.
These technical specifications form the basis of an important guide known as CCN STIC-140 Annex F.11. This guide outlines the regulations that video identification tools must adhere to when remotely verifying someone’s identity using video. These regulations are in accordance with the guidelines established in Ministerial Order ETD/465/2021, which covers the use of video for issuing qualified electronic certificates.
CCN-STIC Guide 140 is issued by the Spanish National Cryptologic Centre (CCN), which establishes security requirements for classified information systems. Annex F.11 of this guide focuses on video-identification tools used for remote identity verification and establishes the technical requirements that these tools must meet, defining two types of identification processes
Unassisted or asynchronous process
In this case, the operator does not speak or interact directly with the user. Instead, they review information stored in databases and information systems. They have a control panel that displays all the evidence, such as images and videos, and decide whether the identification is valid or not. There is no real-time communication with the user; everything is based on data from a previous video-identification process.
Assisted or synchronous processing
Here, the operator communicates with the user via a real-time video call. During the video call, the operator makes a decision based on the tool’s score, a review of the evidence, and their evaluation of the conversation. All data, including the identification result, is recorded in the system and stored in a database.

Let’s go one step further by talking about the EU Digital Identity Wallet
As we have commented, identity proofing is a key process to ensure that a person is who they claim to be in the digital environment. In this context, the EU Digital Identity Wallet emerges as a tool designed to verify our identity securely and efficiently through advanced methods. Although its full implementation is still underway, this digital wallet aims to become a platform for securely storing, managing, and sharing our digital credentials, covering everything from a driver’s license to academic degrees and banking information. This solution ensures that only the wallet holder has access to their data and that only the necessary information is shared.
This European wallet plans to incorporate advanced authentication methods, such as biometrics and multifactor verification, which will provide additional layers of security. Thus, each action taken with the wallet will be supported by a robust validation process, ensuring data protection and privacy.
This comprehensive approach to identity proofing will allow users, once it is fully ready, to access a wide range of public and private services and share documents quickly and in a controlled manner. For example, the wallet will enable users to send an academic degree to a company or sign contracts in a binding way.
Nevertheless, by relying on common technical standards throughout the European Union, the tool will be interoperable across all member countries. This means that, regardless of your location, you will be able to access digital services and share your credentials with validity anywhere in the EU.

MobbScan, your trusted tool for Identity Proofing
Our innovative tool, MobbScan, has stood out in the market by receiving approval and inclusion in the Catalogue of Information and Communication Technology Security Products and Services (CPSTIC). This signifies that MobbScan complies with the highest security standards established by the National Cryptologic Centre (CCN) in the HIGH category of the National Security Scheme (ENS).
The HIGH category of the ENS guarantees that MobbScan has successfully passed rigorous security tests and meets the highest cybersecurity standards. This allows us to provide identity proofing services securely and in compliance with regulations.
In summary, MobbScan is the superhero ensuring that everyone in the digital universe is who they claim to be
Write to us if you want to implement a verification system that allows you to perform a robust identity proofing process both asynchronously (unattended video) and synchronously (video call).

I’m a Software Engineer with a passion for Marketing, Communication, and helping companies expand internationally—areas I’m currently focused on as CMO at Mobbeel. I’m a mix of many things, some good, some not so much… perfectly imperfect.

GUIDE
Identify your users through their face
In this analogue-digital duality, one of the processes that remains essential for ensuring security is identity verification through facial recognition. The face, being the mirror of the soul, provides a unique defence against fraud, adding reliability to the identification process.




