When we hear the term “multimodal,” it often brings to mind transportation. This concept involves using a combination of different methods, such as road, rail, sea, and air transport, to move goods from one location to another.
This system relies on integrating various transport modes, each offering unique advantages: road transport is efficient, rail has a large capacity, sea freight is cost-effective, and air transport is immediate. In the context of international trade, elements like Incoterms regulate the responsibilities and risks at each stage of the journey. This demonstrates how combining different modalities can optimise processes, ensuring products reach their destinations smoothly.
Applying this concept to digital security prompts us to explore the potential for using a similar approach in identity verification. Specifically, it involves using various biometric data to address the limitations of individual systems, such as preventing fraud, while creating an increasingly inclusive and user-centered environment. So, what opportunities could the integration of multiple biometric modalities present in transforming digital identity verification?
Let’s explore this.
The origin of multimodal biometrics
The rise of multimodal biometrics is largely driven by the need to overcome the limitations inherent in unimodal systems, which have traditionally relied on verifying identity based on a single biometric feature. While these early systems have been effective in certain contexts, they have presented some challenges.
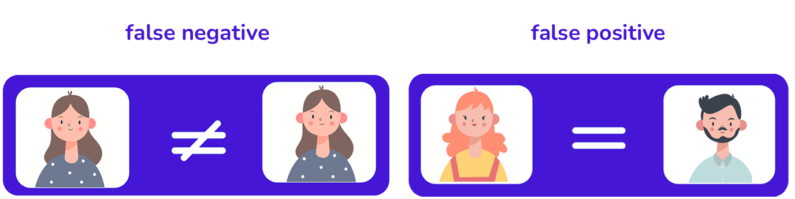
Among these challenges are intraclass variations, which occur when biometric data collected at different times are not identical, potentially leading to false rejections. Additionally, class similarity, which arises when the characteristics of different individuals overlap, has increased the risk of false acceptances. Other obstacles include non-universality, which excludes those who cannot provide the required features.
Technological advancements have addressed these limitations by incorporating new biometric modalities such as voice and facial recognition and, most importantly, by integrating multiple identifiers into a single system.
Therefore, multimodal biometrics has emerged as a response to the demand for more secure authentication methods. It leverages the complementarity of various features to optimise accuracy. By combining biometric information from different sources, a more comprehensive solution is provided, capable of mitigating the issues associated with using only one characteristic.
This evolution has been propelled by advances in machine learning algorithms, image processing, and data fusion techniques, which have enabled the development of more integrated and resilient systems against fraud attempts. Thus, multimodal biometrics stands as an alternative that combines the strength of multiple identifiers to offer a higher degree of security in personal authentication.
What is multimodal biometrics?
Multimodal biometrics is defined by the combined use of multiple biometric features in verifying an individual’s identity, representing a significant advancement in the field of identity verification. Unlike traditional systems that rely exclusively on a single data point, this approach allows for the integration of information from various sources.
The integration of multiple modalities broadens the spectrum of available data and helps to reduce errors linked to variations in sample quality or similarities between individuals.
This methodology is especially useful for addressing the problem of non-universality, as using multiple features ensures broader population coverage. Furthermore, multimodal biometrics is effective in combatting identity theft attempts, as it is quite difficult for an impostor to replicate several biometric traits of a genuine user simultaneously.
How a multimodal biometric system works
The operation of a multimodal biometric system follows a structure similar to traditional systems. The process begins with the sensor module, which captures the necessary biometric modalities, such as voice patterns or facial features. This data is then transmitted to the feature extraction module, where the relevant elements of each modality are identified to generate a compact and precise representation.
Next, the system employs the comparison module to contrast these features with the previously stored templates. This step is important for identifying similarities or differences that allow for identity authentication.
The advantage of using multiple sources is that, in the event of a failure in one modality, the system can rely on others to continue functioning reliably.
Finally, the decision-making module determines whether the individual is accepted or rejected based on the comparison results.
It is also important to note that a liveness detection is a crucial component of such systems, as it ensures that the biometric samples originate from a real person and not a forgery.

Feel free to text us if you’re looking to authenticate your users in digital environments and prevent fraud with a multimodal biometric solution featuring real-time liveness detection, feel free to reach out to us.

I am a curious mind with knowledge of laws, marketing, and business. A words alchemist, deeply in love with neuromarketing and copywriting, who helps Mobbeel to keep growing.

PRODUCT BROCHURE