Amid the wave of digital transformation, companies, public bodies, and other organisations do not need to see each other physically to establish business relationships. That is why different electronic signature methods have emerged to identify people remotely. Among them, we find the advanced electronic signature. The advanced electronic signature (AES) is a secure and legally binding way to sign digital documents. AES uses cryptographic technologies to authenticate the identity of the signer and ensure the integrity of the document.
In this blog post, we want to delve into the Advanced Electronic Signature (AES), emphasising different aspects such as its increased security, the requirements that must be met to be considered advanced, or what the signature process would be like depending on the technology used.
But what is the Advanced Electronic Signature?
The Advanced Electronic Signature is a set of electronic data registered or attached to a data message able to identify its author or signer.
Furthermore, an advanced electronic signature must be created using means that only the holder of the signature maintains under his control.
This type of signature offers a higher level of security than the simple electronic one and achieves a perfect balance between security and usability, giving the process total legal validity.
Find out different electronic signature types here
How to sign using Advanced Electronic Signature?
Based on the technology used to sign, we can find different types of advanced electronic signatures and signature procedures depending on the technology used to sign:
OTP Signature (One Time Password)
When using the OTP signature method, the customer receives an email with a link to the document to be signed. Once the document has been reviewed, the signature process will start by clicking on a button.
Then, the customer will receive a code (a numerical single-use code with a limited timespan validity) on his mobile phone through an SMS or email. This code OTP would be used as a consent token in the signature procedure.
By entering it, the customer signs the reviewed document. Besides, in the process all possible client-side information is captured: name, telephone number, signature device, signature timestamp, access IP, and so forth.
Biometric Signature
Contrary to the procedure followed in the OTP signature, you will not use either a temporary code or something you own (ex: our mobile phone) in your biometric signature.
The process uses your own biometric features to sign, in other words, it uses something that you are instead of something that you have.
Within the biometric signature, you could find different types such as handwritten biometric signatures, voice signatures, or fingerprint signatures.
Handwritten biometric signature
One of the most well-known signatures is the handwritten biometric signature. It allows signing digital documents just as you do on paper: just using your handwritten signature on a device with touch screen capabilities (iPad, tablets, smartphones, pen tablets).
It has total legal validity and there is no need to use any paper at all.
Voice biometric signature
The voice biometric signature works by encrypting and embedding your voice in the electronic document to be signed.
The user must make a voice recording as a first step. After that, the biometric data of the recording will be encrypted and embedded in the document and will act as biometric evidence. This evidence will allow verifying the identity and authorship of the signature.
Fingerprint biometric signature
A fingerprint biometric signature performs the signature by embedding the biometric data of a fingerprint in the document to be signed.
Unlike the other methods, this procedure requires the existence of specific hardware that allows the minutiae of the fingerprint to be read and extracted. This functionality is ideal for assisted environments in which the signatory signs in person.
Can a biometric signature be forged?
Forging our biometric signature is extremely complicated because there is a process which generates a pair of asymmetric keys (composed of a public key and a private key) before a trusted third party.
This process is accomplished before starting the deployment of the project in production.
These are some of its features:
- The private key remains in the custody of the trusted third party, which ensures that no one will have access to it unless a claim process arises and both parties request it or there is a court injunction.
- The public key is delivered to the client.
- In our case, this public key is bundled in MobbSign’s SDK which will be distributed to the mobile devices on which the biometric signature will be performed.
- It ensures that none of the parties signing the document, including the client, can access the original signatures, and modify or extract them.

Requirements for Advanced Electronic Signature
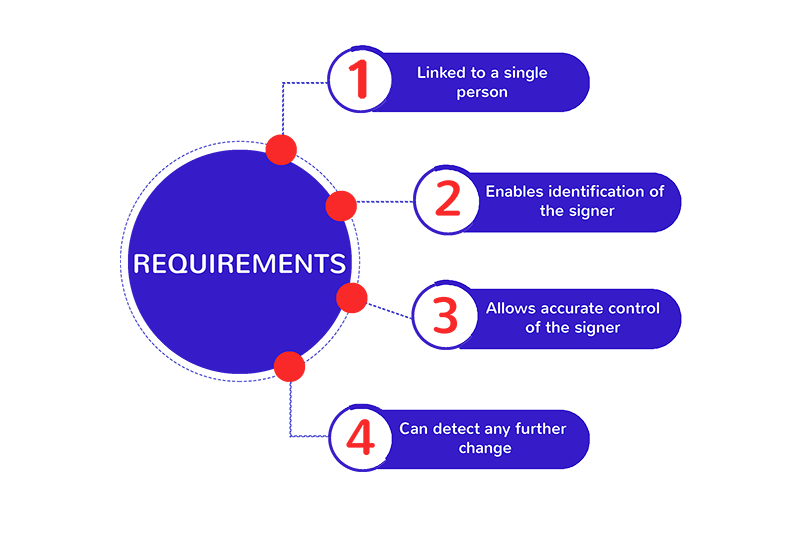
An electronic signature is considered advanced when it meets a series of requirements which are embodied in Article 26 of the eIDAS Regulation. These are:
- The signature must be uniquely linked to the person signing.
- It must allow the identification of the signer.
- Thanks to the use of electronic signature creation data, the signature is created with a high level of confidence under the sole and exclusive control of the signatory.
- It should be linked to the data signed therewith in such a way that any subsequent modification in the data can be detected.
eIDAS legal framework
Regulation (EU) No 910/2014 introduced the first cross-border framework for Electronic Identification and Trust Services (eIDAS) in the EU. It allows EU citizens to sign in every EU country using means of electronic identification (eID) issued in their home country.
It was promulgated on July 23, 2014, by the European Parliament and the Council of European Union abolishing the previous directive (Dir. 1999/93/EC).
eIDAS is more than a law. It is a way of building business and confidence among EU Member States, enabling cooperation and growth within the digital environment.

What is the Mobbeel biometric signature verification process?
Disputes over the validity of an electronically signed document are not rare and when they happen Mobbeel resorts to the signature verification process. This dispute resolution procedure consists in extracting biometric information to verify both the integrity of the document as the authenticity of the signature.
Roughly speaking, the steps for this procedure are:
- The signed document in PDF format is self-contained, which means that it includes all the information necessary to verify its integrity and the authenticity of the signatures.
- To extract the biometric characteristics of the signature and verify the identity of the document, it is necessary that, upon injunction or by agreement between the parties, the notary or the third party decrypts this data using the private key which has remained in custody. The solution includes a tool that extracts the data from the PDF and makes it available to the calligraphic expert to facilitate the process.
- Other signatures are used as references and new samples could be taken under the supervision of a forensic handwriting expert.
- The expert compares the newly acquired signatures with the ones extracted from the document, using the large amount of data available.
- Then, the expert issues a report with the decision of whether or not the signature on the document corresponds to the person making the claim.
Advantages of using an Advanced Electronic Signature
This kind of signature provides these benefits:
- Saves direct storage, paper, and courier costs.
- Reduces time and effort.
- Allows to sign anywhere and at any time.
- Enables the collection and storage of the signed document in digital format with the benefit of a greater control.
- Document localisation is faster and easier Improves user experience.
- Greatly improves security, since it uses means that are under the exclusive control of the owner.
Advanced Electronic Signature in your industry
Mobbeel works with companies from multiple industries around the globe.
The electronic signature digitalises the signature process allowing it to be done remotely, reducing costs, and eliminating paper, but there are many other benefits of its use in each industry. In this way:
In the financial/banking/fintech or cryptocurrencies sector, the main needs covered with any of Mobbeel’s digital identity verification solutions are regulatory compliance (especially in opening accounts), improvement in user experience, greater security, reduction of contact in face-to-face procedures and increased agility in the customer service process.
Some improvements to Travel / Tourism / Hotels are to provide a convenient user experience, increase agility in check-in processes, reduce contact in face-to-face procedures, and the signing of documents digitally.
In Telecommunications, they are the regulatory compliance in the hiring of new products or SIM cards, the improvements in user experience, the greater security, the increased agility, and the prevention of identity theft fraud.
The facilitation in the management of the process of signing documents through their digitisation and verification of the identity of sellers or landlords are some of the advantages of using AES in Real Estate.
We also work with other industries such as Sharing Economy, Mobility, Online Gaming, and Gambling.
If you are looking to solve some of the problems that we have previously exposed, do not hesitate to contact us and discover what our technology can do for you.

I’m a Software Engineer with a passion for Marketing, Communication, and helping companies expand internationally—areas I’m currently focused on as CMO at Mobbeel. I’m a mix of many things, some good, some not so much… perfectly imperfect.

PRODUCT BROCHURE
Discover our biometric signature solution
Provide your customers with the option to easily and ecologically sign documents anywhere and anytime using our biometric signature, which is considered an Advanced Electronic Signature with full legal validity.