Proof o life is a document issued by the Civil Registry that certifies that a person is alive at a specific time. This certificate is essential for various legal and administrative procedures, especially in the context of pensions, insurance, and other social benefits. With the evolution of technology and the growing need for security in digital processes, new ways to confirm a person’s liveness have emerged: liveness detection.
Liveness detection is an advanced technology that validates that a person is alive and goes beyond confirming that the user is who they claim to be by using biometric methods during digital onboarding processes or authentication. These tests are essential for preventing identity fraud and ensuring that only authorised persons access the corresponding platforms.
Algorithms and liveness detection, a contemporary solution
Initially, liveness detection was carried out in person, where people had to physically appear in offices to certify that they were alive. This traditional method, though effective, was often cumbersome and required time and effort both from the subject and the organisations and companies.
With the digitalisation of processes, the need arose to find more efficient and secure methods. The first innovations included the use of electronic records and databases to verify a person’s existence, but these initial solutions lacked robust mechanisms against identity fraud.
The real change came with the development of advanced biometric technologies, which led to what we know as liveness detection. The first generation of liveness detection was active liveness detection, which required users to perform specific actions, such as blinking or moving their heads from side to side, to confirm their authenticity.
Nevertheless, these mechanisms presented certain challenges in terms of usability. It was then that passive liveness detection was developed, capable of confirming a person’s authenticity without requiring additional actions, simply by analysing biometric characteristics in real-time.
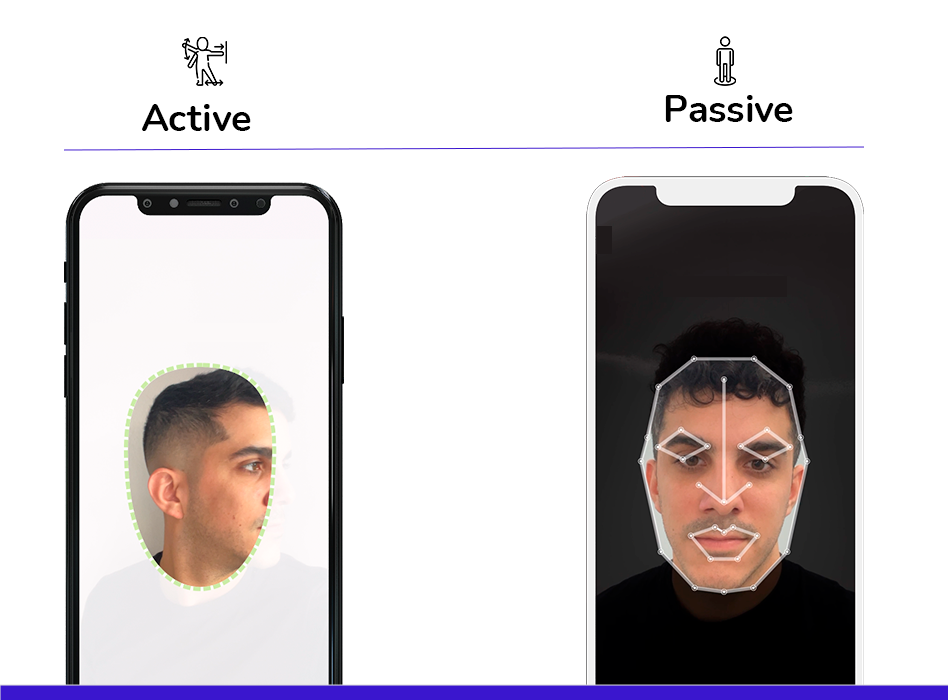
Let’s compare passive and active liveness detection
When it comes to choosing between passive and active liveness detection, it is necessary to conduct a comparison considering aspects such as security, user experience, and efficiency.
Security
Active liveness detection:
Active detection mechanisms require the user to perform specific actions, such as blinking, smiling, or moving their head. Active liveness can be vulnerable to sophisticated presentation attacks if the algorithm is not well-calibrated to detect subtle variations in user behaviour or possible artefacts.
Passive liveness detection:
Passive liveness analyses biometric features in real-time without requiring active user interaction, being effective in detecting genuine signs of life. Passive liveness detection is not perceived by the user and, therefore, does not provide clues to impostors on how to mimic expressions with animation software.
User experience
Active liveness detection:
The required interaction can negatively impact the user experience, as some users may find the required actions difficult or the movements uncomfortable.
Passive liveness detection:
It offers a smoother and more usable user experience, as it does not require any additional action from the user. This results in a less intrusive process.
Speed and operational efficiency
Active liveness detection:
Active liveness detection requires the user to follow specific instructions and then perform the requested action. This process can be slower, increasing the total verification time.
Passive liveness detection:
The user does not need to follow instructions or perform any actions, as these mechanisms rely on the user’s natural behaviour. This reduces the average time taken for this step within the process.
So, which liveness detection is better?
Our recommendation leans towards passive liveness detection.
This type of liveness uses advanced facial recognition algorithms and real-time biometric analysis to detect signs of life. These systems are designed to identify fraud attempts through static images or pre-recorded videos, ensuring robust protection against identity theft.
This approach offers a much smoother and less intrusive user experience compared to active liveness. By not requiring the user to perform specific actions like moving their head side to side, any potential friction during the process is eliminated. This provides higher levels of accessibility for all users, including those with physical or technological limitations. Liveness detection is performed quickly and naturally, positively impacting the user and reducing the abandonment rate and frustration.

Passive liveness detection employs advanced facial recognition algorithms and real-time biometric characteristic analysis to detect signs of life. They use deep learning image recognition techniques to distinguish a real face from an artefact, evaluating details such as involuntary movements.
One of the best advantages of this method is that it runs in the background during the face capture process, requiring only a single frame or micro-video to determine if the user is real and alive. This makes it difficult to counterfeit, even with 3D masks or deepfakes. Additionally, it requires minimal cooperation from the user, as they only need to look at the camera, eliminating the need to perform a set of actions. Generally, this method is faster because it does not depend on the user performing specific movements or having to follow usage instructions.

I am a curious mind with knowledge of laws, marketing, and business. A words alchemist, deeply in love with neuromarketing and copywriting, who helps Mobbeel to keep growing.

GUIDE
Identify your users through their face
In this analogue-digital duality, one of the processes that remains essential for ensuring security is identity verification through facial recognition. The face, being the mirror of the soul, provides a unique defence against fraud, adding reliability to the identification process.




